Guide to Fabricated Metal Enclosures: Boxes, Bins, Cages, Containers, Panels and Cabinets
 Fabricated metal enclosures are essential infrastructure across industries, providing protection, organization, and structural support for equipment, electronics, and sensitive components. From weatherproof electrical junction boxes protecting power systems in harsh outdoor environments to precision-engineered control panels meeting UL 508A certification standards, these enclosures serve critical functions that directly impact equipment reliability, safety compliance, and operational efficiency.
Fabricated metal enclosures are essential infrastructure across industries, providing protection, organization, and structural support for equipment, electronics, and sensitive components. From weatherproof electrical junction boxes protecting power systems in harsh outdoor environments to precision-engineered control panels meeting UL 508A certification standards, these enclosures serve critical functions that directly impact equipment reliability, safety compliance, and operational efficiency.
Unlike off-the-shelf catalog enclosures with fixed dimensions and generic specifications, custom fabricated metal enclosures are engineered to exact requirements—tailored dimensions, specific material properties, integrated mounting systems, custom cutouts for connectors and displays, and finishes designed for particular environmental conditions. This customization capability makes fabricated enclosures the solution of choice for OEMs, industrial manufacturers, and facilities requiring protection solutions that standard products simply cannot provide.
This comprehensive guide examines the types of fabricated metal enclosures available, material selection considerations, customization options, industry standards and compliance requirements, and the critical factors that determine whether an enclosure will perform reliably over its intended service life.
Types of Fabricated Metal Enclosures and Their Applications
Understanding the distinct categories of metal enclosures helps specify the right solution for your application’s protection requirements, environmental conditions, and functional needs.
Metal Boxes: Electrical and Weatherproof Protection
Metal boxes represent the most common category of fabricated enclosures, providing essential protection for electrical systems, wiring, and junction points.
Electrical Junction Boxes: These enclosures house electrical connections, terminal blocks, and wiring terminations in industrial, commercial, and utility applications. Junction boxes protect connections from physical damage, prevent accidental contact with live electrical components, and contain arcing or sparking that could ignite combustible atmospheres in hazardous locations.
Industrial junction boxes must meet National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) ratings appropriate to their installation environment. NEMA 1 enclosures provide basic indoor protection against incidental contact. NEMA 3R boxes offer outdoor protection against rain and ice formation. NEMA 4X enclosures provide corrosion-resistant protection against water ingress, suitable for food processing, chemical plants, and coastal environments.
Weatherproof Boxes: Outdoor applications require enclosures designed specifically to prevent moisture ingress, resist UV degradation, and maintain gasket sealing integrity through temperature cycling. Weatherproof boxes incorporate gaskets between mounting surfaces, recessed mounting hardware that doesn’t compromise the sealed envelope, and drainage systems that prevent water accumulation.
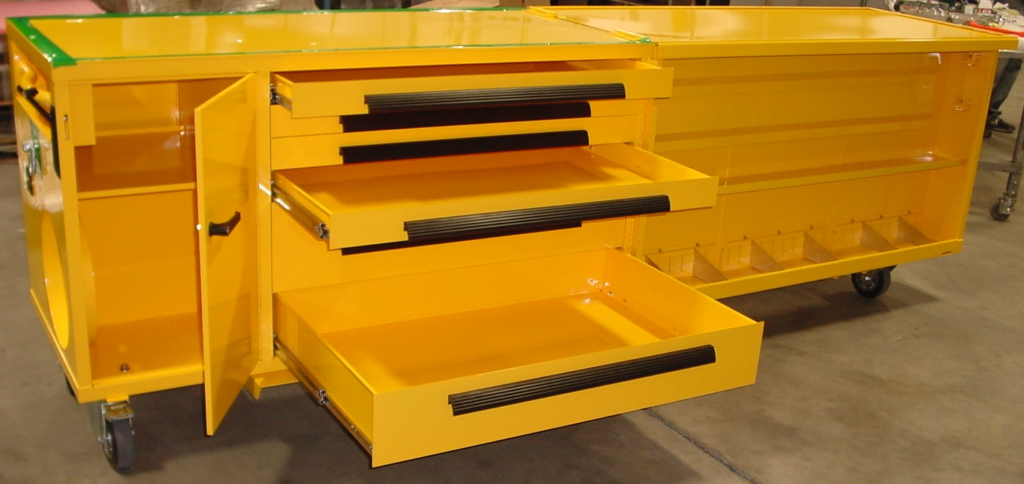

Commercial and Industrial Toolboxes: Specialized industries require toolboxes designed for specific tool sets and operational requirements. Aviation maintenance toolboxes incorporate FOD (Foreign Object Debris) prevention features including foam tool layouts that immediately reveal missing tools. Automotive racing team boxes combine secure storage with quick-access organization for pit crew efficiency. Industrial plant maintenance boxes integrate lifting eyes for crane handling and heavy-duty casters for shop floor mobility.
Custom fabricated toolboxes can incorporate features impossible in standard commercial units: integrated charging stations for battery-powered tools, humidity-controlled compartments for precision instruments, and organization systems matched to specific tool inventory.
Metal Cages and Chassis: Open-Frame Protection
When equipment requires protection while maintaining visibility, ventilation, or access, cages and chassis provide the optimal solution.

Modern server rack fabrication incorporates cable management systems, adjustable mounting rails for varying equipment depths, and provisions for both top-to-bottom and front-to-rear airflow configurations. High-density installations may require reinforced construction to support 1,000+ pounds of equipment in a single rack.
Card Cages for Testing Equipment: Research and development laboratories, aerospace testing facilities, and electronics manufacturing operations use card cages to secure and test printed circuit boards during development cycles. These enclosures provide mechanical support, electrical grounding, EMI/RFI shielding, and organized signal routing for prototype testing.
Precision card cages maintain tight tolerances for card alignment, incorporate backplane mounting systems for interconnections between cards, and provide access hatches for probing test points during troubleshooting. The fabrication quality directly impacts testing reliability—poorly aligned card guides cause insertion problems, inadequate grounding creates signal integrity issues, and thermal management deficiencies lead to component failures during extended testing.
Metal Containers: Secure Storage and Transport
Metal containers provide robust protection for materials requiring security, environmental protection, or regulatory compliance during storage and transportation.
Storage Containers with Security Features: Construction sites, remote facilities, and high-value inventory applications require containers with tamper-resistant designs. Fabricated metal containers can incorporate concealed hinges that prevent pin removal, recessed lock housings protecting padlocks from bolt cutters, and reinforced corners resisting pry bar attacks.
Security container fabrication goes beyond simple heavy-gauge construction—welded reinforcement plates at lock points, internal locking mechanisms activated only when the container is closed, and alarm system provisions transform standard containers into genuine security enclosures.
Temperature-Controlled Containers: Pharmaceutical logistics, specialty chemical transport, and food distribution require containers maintaining stable internal temperatures during transit. These enclosures incorporate insulation systems (spray foam, vacuum panels, or phase-change materials), interior lining materials compatible with contents, and provisions for monitoring systems tracking temperature throughout transport.
Fabricating temperature-controlled containers requires understanding thermal bridging—how metal framework conducts heat around insulation, compromising temperature stability. Proper design minimizes thermal bridges through material selection and construction techniques specific to insulated enclosure fabrication.
Metal Panels: Functional and Protective Surfaces
Metal panels serve both aesthetic and functional purposes in building systems, industrial enclosures, and equipment installations.
Fire-Resistant Panels: Industrial and commercial construction applications specify fire-rated panels protecting mechanical and electrical systems. These panels achieve fire resistance ratings through material selection (steel gauge and composition), construction methods (welded versus mechanical fastening), and approved assembly configurations tested to ASTM E119 or UL 263 standards.
Fire-rated enclosures aren’t simply thicker metal—they’re engineered assemblies with documented fire resistance performance. Modifications like adding penetrations or changing fastener patterns can void fire ratings, making proper fabrication specifications critical to maintaining certification.
Soundproof Panels: Manufacturing facilities, data centers, and building mechanical rooms require noise attenuation without sacrificing access to equipment. Sound-dampening panels combine mass (heavy-gauge steel providing transmission loss), absorption (acoustic insulation materials), and damping (constrained-layer construction reducing panel resonance).
Effective acoustic enclosures require attention to flanking paths where sound bypasses panels through gaps, ventilation penetrations, or structural connections. Fabrication quality—particularly gasket sealing and panel-to-frame fit—determines whether theoretical acoustic performance translates to real-world noise reduction.
Metal Cabinets: Enclosed Storage and Control Systems
Cabinets provide complete enclosure with door access, making them ideal for electrical controls, instrumentation, and secure storage applications.
Explosion-Proof Cabinets: Facilities handling volatile materials, combustible dusts, or flammable atmospheres require enclosures certified to contain internal explosions without propagating ignition to surrounding atmospheres. These cabinets meet NEC Article 500 requirements for hazardous location classifications, achieving certification through heavy-wall construction, flame-path joints that cool expanding gases below ignition temperature, and hardware rated for hazardous locations.
True explosion-proof fabrication requires specialized knowledge of joint configurations, surface finish requirements, and testing protocols. These aren’t simply heavy-duty enclosures—they’re precision-fabricated pressure vessels with documented performance in explosive atmosphere testing.
Well-designed modular systems balance flexibility with structural integrity—mounting provisions must maintain strength across various configurations, panel interfaces must align precisely regardless of assembly sequence, and door hardware must accommodate different door sizes within the system.
Industrial Metal Bins: Material Handling and Storage
Manufacturing operations, warehouse facilities, and recycling operations depend on metal bins designed for durability and efficient material handling.
Heavy-Duty Industrial Bins: Component manufacturing, automotive assembly, and metal fabrication facilities require bins withstanding forklift handling, overhead crane lifting, and impacts from heavy parts. These bins incorporate reinforced edges, corrugated sides providing structural rigidity, and lifting provisions engineered for specified load capacities.
Industrial bin fabrication considers the complete lifecycle—how bins stack when empty for efficient storage, how lifting equipment engages for safe handling, how contents are discharged (tilt mechanisms, bottom doors, forklift tine slots), and how bins resist deformation over thousands of loading cycles.
Recycling Bins for Industrial Use: Scrap metal collection, plastic recycling, and waste segregation operations require bins sized for material types, handling equipment, and processing volumes. Large-volume industrial recycling bins feature drain holes preventing water accumulation, identification labeling systems visible from forklift operator sightlines, and construction materials selected for contents (stainless steel for corrosive materials, heavy carbon steel for abrasive scrap metal).
Metal Carts: Mobile Equipment and Material Transport
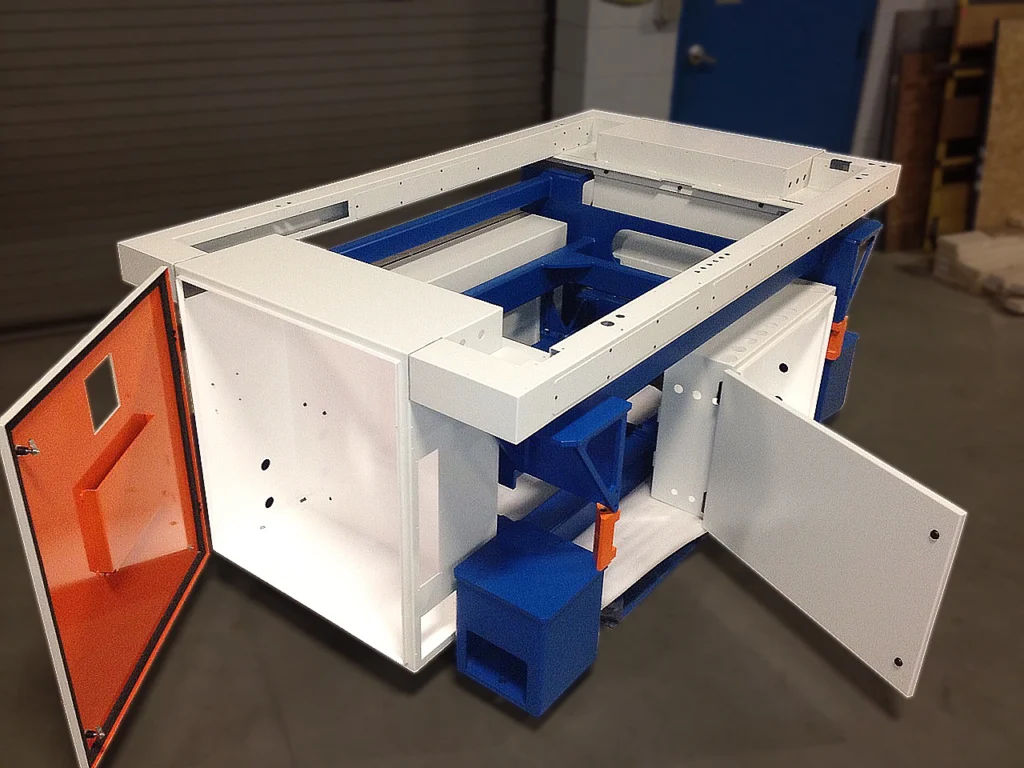

Ergonomic Tool Carts: Assembly line operations, maintenance departments, and manufacturing cells benefit from carts designed to minimize worker fatigue and maximize productivity. Ergonomic cart design considers handle heights for comfortable pushing/pulling, wheel configurations providing maneuverability in confined spaces, and shelf/drawer arrangements eliminating repetitive bending or reaching.
Advanced tool cart fabrication incorporates features like ESD-safe coatings for electronics assembly, magnetic tool retention preventing loss during transport, and locking mechanisms allowing carts to serve as secure mobile storage when not in use.
Medical Supply Carts: Healthcare environments require mobile storage meeting infection control standards, providing secure medication storage, and integrating with electronic health record systems. Medical cart fabrication uses materials compatible with hospital-grade disinfectants, incorporates antimicrobial powder coat finishes, and provides locking compartments meeting DEA controlled substance security requirements.
Material Selection and Properties
Choosing the correct base material fundamentally determines enclosure performance, longevity, and suitability for the intended application environment.
 Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Stainless steel enclosures excel in applications where corrosion resistance, cleanability, or aesthetic appearance are priorities.
Corrosion resistance: The chromium content in stainless steel (minimum 10.5%) forms a passive oxide layer that self-heals when scratched, providing inherent corrosion protection without coatings. Type 304 stainless offers excellent corrosion resistance for most environments. Type 316 stainless, with added molybdenum, provides superior resistance to chlorides—critical for coastal installations, road salt exposure, or chemical processing environments.
Applications: Food processing equipment enclosures, pharmaceutical manufacturing controls, outdoor coastal installations, clean room equipment, and any application where enclosures must withstand regular wash-down with sanitizing chemicals.
Considerations: Stainless steel costs significantly more than carbon steel (typically 3-5x material cost), requires specialized welding procedures to maintain corrosion resistance, and work-hardens during fabrication, requiring more powerful equipment and consuming more processing time.
Carbon Steel: Structural Strength and Cost-Effectiveness
Carbon steel (also called mild steel or low-carbon steel) provides excellent strength-to-cost ratio, making it the default choice for most structural and general-purpose enclosures.
Strength characteristics: Carbon steel’s higher yield strength compared to aluminum allows thinner material achieving equivalent structural rigidity, important for large enclosures where material costs and weight compound with size. Cold-rolled steel provides tighter thickness tolerances and better surface finish than hot-rolled material, though at higher cost.
Applications: Control panels, electrical cabinets, industrial equipment housings, storage containers, structural frames, and any indoor application where corrosion resistance isn’t the primary concern.
Considerations: Carbon steel requires protective finishing (powder coating, wet paint, galvanizing) to prevent rust in any environment with moisture exposure. Welding carbon steel is straightforward with common equipment and processes. Material costs are lowest among structural metals, making carbon steel the economical choice for larger fabrications.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Natural Corrosion Protection
Aluminum’s combination of light weight (one-third the density of steel) and natural corrosion resistance makes it valuable for specific applications despite higher material costs.
Corrosion properties: Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer providing corrosion protection without coatings, though this protection is less robust than stainless steel’s passive layer. In marine or industrial atmospheres, aluminum may require anodizing or coating for long-term durability.
Applications: Aerospace equipment enclosures where weight is critical, portable equipment cases requiring frequent handling, heat sink applications leveraging aluminum’s thermal conductivity, and electrical enclosures benefiting from aluminum’s non-magnetic properties.
Considerations: Aluminum’s lower strength requires thicker material or reinforcement ribs to achieve equivalent rigidity compared to steel. Welding aluminum requires different equipment, procedures, and expertise than steel welding. Dissimilar metal contact between aluminum and steel creates galvanic corrosion requiring isolation or protective treatments.
Customization Features and Options
The value of fabricated enclosures lies in the ability to engineer specific features matching application requirements—customization that catalog products cannot provide.
Protective Finishes: Enhancing Durability and Appearance
Surface finishing transforms raw metal into a protective system designed for specific environmental conditions and aesthetic requirements.

EVS Metal operates in-house powder coating facilities, providing color consistency, fast turnaround, and quality control impossible when outsourcing finishing. Powder coat finishes are available in countless colors, textures (smooth, textured, metallic), and gloss levels, allowing enclosures to match equipment aesthetics or meet corporate branding requirements.
Galvanizing: Hot-dip galvanizing coats steel with zinc, providing exceptional corrosion protection for outdoor structures, utility applications, and harsh industrial environments. The zinc coating sacrifices itself to protect the base steel (cathodic protection), meaning even scratches exposing base metal remain protected. Galvanized enclosures commonly serve utility infrastructure, outdoor telecommunications equipment, and industrial material handling.
Anodizing: Anodizing aluminum creates a thick, hard oxide layer integrated with the base metal (not a coating applied to the surface). Anodized finishes provide excellent wear resistance, corrosion protection, and can incorporate dyes creating colored finishes. Aerospace, electronics, and architectural applications commonly specify anodized aluminum enclosures.
The selection among finishing options depends on environmental exposure, required durability, aesthetic requirements, and budget. For more details on finishing options and their applications, see our guide to metal finishes and applications.
Gaskets and Seals: Environmental Protection
Achieving NEMA or IP-rated environmental protection requires proper gasket design and installation—without effective sealing, even the best-fabricated enclosure fails to protect contents.
Gasket materials: Closed-cell foam gaskets provide excellent compression set resistance and work across wide temperature ranges for general-purpose indoor applications. Silicone rubber gaskets withstand extreme temperatures (-60°F to 400°F) and resist UV degradation for outdoor applications. EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber excels in weather resistance and ozone exposure.
Gasket configuration: Continuous gaskets with vulcanized corners eliminate potential leak paths at corners where separate gasket pieces meet. Gasket compression must be controlled through enclosure design—too little compression allows leaks, excessive compression causes gasket extrusion and premature failure. Door enclosures require captured gasket designs preventing displacement during door operation.
Ventilation and Thermal Management
Electronics enclosures must manage heat dissipation without compromising environmental protection or allowing contaminant ingress.
Passive ventilation: Louvered panels positioned for natural convection (low inlet, high outlet) provide cooling without moving parts. Louver design balances airflow with environmental protection—fine mesh screens prevent insect ingress while minimizing airflow restriction.
Active cooling integration: Many applications require fan-forced cooling for adequate heat dissipation. Enclosure fabrication must accommodate fan mounting, cable routing for fan power, and intake/exhaust configurations matching equipment airflow requirements. Filter housings at intake ports protect components from airborne contaminants while requiring maintenance access for filter changes.
Heat dissipation design: High-power electronics may require specialized thermal management beyond simple ventilation. Heat pipe integration, conductive mounting plates transferring heat to enclosure exterior, or liquid cooling provisions represent advanced thermal design features available through custom fabrication.
Modular Design and Expandability
Equipment that evolves over time benefits from enclosure designs accommodating growth and modification.
Standardized mounting provisions: DIN rail mounting for electrical components, threaded inserts for panel mounting, and universal rack-mount provisions allow equipment changes without enclosure replacement. Panel manufacturers appreciate enclosures pre-fabricated with mounting systems matching their assembly processes.
Knockout provisions: Pre-formed knockout areas (partially fabricated openings) allow field personnel to create cable entry points using hand tools, avoiding the expense and delay of returning enclosures to fabrication shops for modifications. Knockout design must prevent moisture infiltration and maintain EMI shielding when opened.
Expandable configurations: Some applications benefit from enclosures designed to accept add-on sections. Modular industrial control panels, for example, may start with basic motor controls and later add process monitoring systems, requiring enclosure expansion without replacing existing infrastructure.
Industry Standards and Compliance Requirements

NEMA Ratings: Environmental Protection Standards
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) standards define enclosure protection levels against specific environmental conditions. Understanding NEMA ratings helps specify appropriate protection without over-engineering.
NEMA 1: Indoor use, protection against incidental contact with enclosed equipment, falling dirt. No protection against moisture. Used for indoor electrical panels in clean, dry environments.
NEMA 3R: Outdoor use, protection against rain, sleet, snow, and ice formation. Allows some water entry that won’t interfere with operation. Common for outdoor electrical service equipment.
NEMA 4 and 4X: Indoor/outdoor use, watertight protection against hose-directed water and splashing. NEMA 4X adds corrosion resistance (typically stainless steel construction). Required for food processing, pharmaceutical, and chemical industry applications subject to wash-down.
NEMA 12: Indoor use, protection against circulating dust, falling dirt, dripping non-corrosive liquids. Used in industrial facilities for electrical controls mounted near machining operations.
For more information about NEMA-rated enclosures, see our comprehensive guide to NEMA-rated metal enclosures.
UL Certification: Safety and Compliance
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification indicates enclosures meet rigorous safety standards, particularly critical for electrical equipment.
UL 508A: Industrial control panels containing electrical components must meet UL 508A requirements covering construction, component ratings, wiring methods, and short-circuit protection. Panel fabricators must operate as UL 508A certified shops, maintaining documentation of construction methods, using UL-recognized components, and following prescribed assembly procedures.
EVS Metal operates as a UL 508A certified fabricator, providing certified control panels meeting NEC requirements for industrial electrical installations. UL 508A certification isn’t simply about the enclosure—it encompasses the complete assembly including internal components, wiring methods, and safety features.
UL 50 and UL 50E: These standards cover enclosures for electrical equipment, defining test methods for evaluating environmental protection, structural integrity, and safety features. UL 50E specifically addresses enclosures for European markets, harmonizing with international IEC standards.
IP Ratings: International Protection Standards
IP (Ingress Protection) ratings provide internationally recognized standards for enclosure protection against solid objects and liquids. IP ratings use a two-digit format: IP6X (first digit = solid particle protection), IPX7 (second digit = liquid ingress protection).
Common IP ratings:
- IP54: Dust protected, protected against splashing water
- IP65: Dust tight, protected against water jets
- IP66: Dust tight, protected against powerful water jets
- IP67: Dust tight, protected against temporary immersion
European and Asian markets typically specify IP ratings rather than NEMA ratings, though general equivalencies exist (NEMA 4 ≈ IP66, NEMA 4X ≈ IP66 with corrosion resistance).
Industry-Specific Requirements
Beyond general standards, certain industries impose additional requirements affecting enclosure design and fabrication.
ITAR Compliance: Fabricators producing enclosures for defense applications must register with ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations), implementing security procedures for controlled technical data and restricting access to foreign nationals. EVS Metal maintains ITAR registration, enabling work on defense-related projects.
Food Industry Standards: Enclosures in food processing facilities must use materials compatible with food contact (stainless steel), feature designs preventing bacterial growth (crevice-free construction, washable surfaces), and withstand aggressive sanitizing chemicals. 3-A Sanitary Standards provide guidance for food industry equipment design.
Pharmaceutical Clean Room Requirements: Enclosures in pharmaceutical manufacturing must meet clean room classifications (ISO 14644-1), using materials that don’t shed particles, featuring smooth surfaces for easy cleaning, and incorporating designs that don’t trap contaminants.
Selecting the Right Industrial or Commercial Fabricated Metal Enclosure
Successful enclosure specification requires systematically evaluating application requirements against available options.
Environmental Conditions Assessment
Indoor vs. outdoor installation: Outdoor enclosures require weather protection (NEMA 3R minimum), UV-resistant finishes, and gasket materials withstanding temperature cycling. Indoor applications may require only basic dust protection (NEMA 1 or 12).
Temperature extremes: Enclosures in high-temperature environments need finishes withstanding heat without degrading. Cold environment installations require gasket materials remaining flexible at low temperatures and may need provisions for heating to prevent ice formation.
Corrosive atmospheres: Chemical plants, coastal installations, and food processing facilities require corrosion-resistant materials (stainless steel, galvanized steel) or protective coatings withstanding specific chemicals encountered.
Physical hazards: Locations with impact risks need reinforced construction or protective barriers. Explosion-proof environments require certified enclosures containing internal explosions.
Equipment Integration Requirements
Mounting systems: Will equipment mount to DIN rail, threaded panels, or custom brackets? Early coordination between enclosure fabricator and equipment supplier prevents costly modifications.
Cable entry methods: How many cables enter the enclosure? What sizes? Are conduit entries, cord grips, or cable glands required? Proper cable entry design prevents moisture infiltration and maintains EMI shielding.
Access requirements: How frequently do technicians need interior access? Full front doors, removable panels, or small access ports each suit different maintenance scenarios.
Future expansion: Will the enclosure need to accommodate additional equipment later? Designing spare capacity into initial fabrication costs less than retrofitting.
Size and Space Constraints
Available installation space: Measure installation location precisely, accounting for door swing clearance, maintenance access, and ventilation airflow.
Equipment dimensions: Allow adequate space for components plus wiring routing, ventilation clearances specified by component manufacturers, and service clearances for maintenance access.
Weight considerations: Will the installed enclosure require structural support? Account for enclosure weight plus equipment weight plus worst-case service loading (technician leaning on enclosure during maintenance).
Budget and Timeline
Custom vs. modified standard: Sometimes modifying a standard catalog enclosure (adding custom cutouts, special finishes, mounting provisions) delivers faster results at lower cost than full custom fabrication. Other times, application requirements make custom fabrication the only viable approach.
Prototype vs. production: First-article enclosures for equipment development may justify simplified construction methods accepting manual operations. Production quantities benefit from jig-fabrication and process optimization reducing per-unit costs.
Lead time requirements: Standard catalog enclosures ship in days, modified standards in weeks, full custom fabrication in weeks to months depending on complexity and shop workload. Critical timeline projects may drive design decisions toward faster-to-fabricate options.
For a comprehensive look at the metal fabrication process from design through delivery, see our guide to contract sheet metal fabrication.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Enclosure Specification
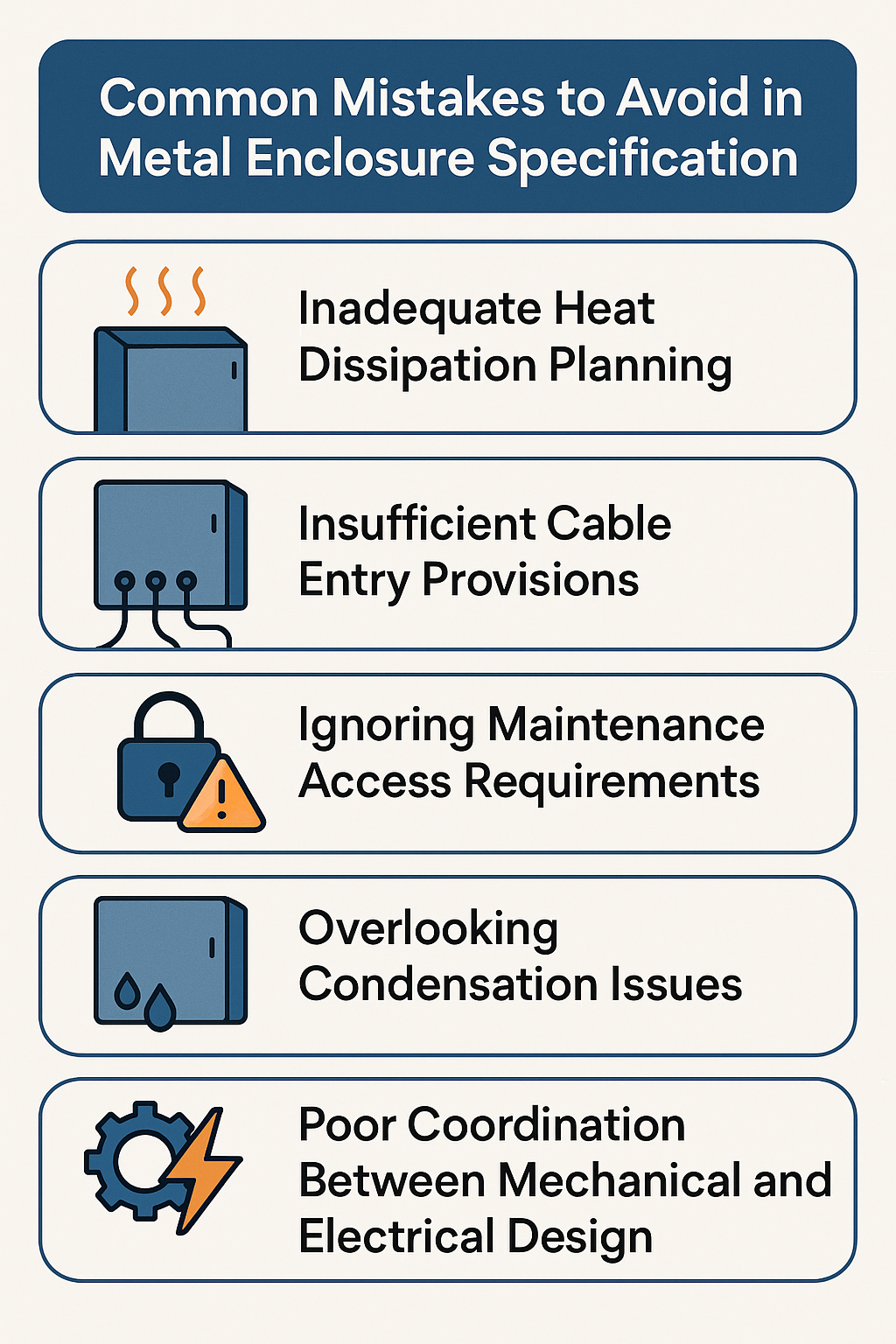
Inadequate Heat Dissipation Planning
Electronics generate heat that must be removed to prevent premature failure. Many enclosure projects underestimate thermal loads or fail to provide adequate ventilation. Calculate actual heat dissipation from enclosed equipment (not just nameplate power ratings), factor in solar heat gain for outdoor enclosures, and design ventilation systems moving sufficient air volume while maintaining environmental protection ratings.
Insufficient Cable Entry Provisions
Underestimating the number, size, or type of cable entries leads to field modifications that compromise environmental ratings and create aesthetic issues. Work with equipment suppliers early to determine all cable entry requirements, allow spare entries for future additions, and specify cable entry methods (conduit hubs, cord grips, cable glands) compatible with installation practices.
Ignoring Maintenance Access Requirements
Enclosures providing inadequate access frustrate technicians and may prevent proper equipment service. Consider which components require regular maintenance (filter changes, adjustments, visual inspection), which require occasional service (component replacement, wiring changes), and design access accordingly. Small access ports for routine maintenance plus large removable panels for infrequent major service often provides optimal balance.
Overlooking Condensation Issues
Temperature differentials between enclosure interior and exterior cause condensation that damages electronics. Outdoor enclosures with air conditioning (common for telecommunications equipment) experience severe condensation without proper vapor barriers. Indoor enclosures in humid environments benefit from thermostatically-controlled heaters maintaining interior temperature slightly above ambient, preventing moisture condensation.
Poor Coordination Between Mechanical and Electrical Design
Mechanical engineers specifying enclosures and electrical engineers designing equipment installations must coordinate closely. Problems arise when enclosure mounting provisions don’t align with equipment mounting patterns, when cable entry locations interfere with equipment placement, or when space allocated for wiring proves insufficient.
EVS Metal: Expert Fabrication of Industrial and Commercial Aluminum and Steel Enclosures
Specifying and fabricating metal enclosures that reliably protect equipment requires deep understanding of materials, manufacturing processes, industry standards, and real-world application challenges. EVS Metal brings over 30 years of precision sheet metal fabrication experience to every enclosure project.
Comprehensive Fabrication Capabilities
EVS Metal operates four facilities across New Jersey, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, and Texas, providing complete enclosure fabrication services:
Precision sheet metal fabrication using advanced laser cutting, CNC punching, CNC forming, and robotic press brake systems delivers tight tolerances and consistent quality across production runs.
CNC machining capabilities enable complex features like precision mounting provisions, threaded inserts, and custom hardware integration impossible with sheet metal processes alone.
Welding and joining using MIG, TIG, spot welding, and specialized processes creates robust assemblies meeting structural and aesthetic requirements.
In-house finishing including powder coating, wet painting, and surface preparation ensures consistent appearance and corrosion protection.
Assembly and integration services transform fabricated enclosures into complete systems ready for installation, including electrical component mounting, wiring, and functional testing.
Engineering Support and Design Optimization
EVS Metal’s engineering team collaborates with customers from concept through production, optimizing enclosure designs for manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, and performance. Services include:
- CAD design and 3D modeling translating concepts into manufacturable designs
- Design for manufacturability (DFM) review identifying potential issues before fabrication
- Prototype development allowing physical testing before committing to production tooling
- Value engineering identifying cost reduction opportunities without compromising functionality
Quality and Compliance
ISO 9001:2015 certification ensures consistent quality management throughout all operations. Specialized certifications include:
- UL 508A certification for industrial control panel fabrication
- ITAR registration enabling defense-related projects
- AS9100 aerospace quality management system compliance
Industries Served
EVS Metal fabricates custom enclosures for customers across multiple sectors including telecommunications, industrial automation, aerospace and defense, medical equipment, renewable energy systems, and commercial building infrastructure. Each industry brings unique requirements that inform our enclosure design and fabrication approach.
For examples of custom fabrication projects, explore our case studies and product samples.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fabricated Metal Enclosures
What NEMA rating do I need for my outdoor enclosure?
The minimum outdoor rating is NEMA 3R, which protects against rain, snow, and ice formation but allows some water entry that won’t interfere with operation. For applications requiring complete water protection (wash-down environments, areas with direct water spray), specify NEMA 4 or 4X. NEMA 4X adds corrosion-resistant materials (typically stainless steel) for coastal environments or chemical exposure. If your enclosure will house sensitive electronics, NEMA 4 or 4X provides better protection despite higher cost.
How do I determine what size enclosure I need?
Start with equipment dimensions, then add clearances on all sides (typically 3-6 inches depending on component type). Account for cable routing space (cables consume more volume than expected), allow clearance for NEC-required working space around electrical components, and ensure ventilation airflow isn’t obstructed. For electrical panels, NEC Article 110.26 specifies minimum working clearances. When in doubt, slightly oversizing the enclosure is less expensive than discovering inadequate space during installation.
What’s the difference between powder coating and wet paint for enclosure finishing?
Powder coating applies dry powder electrostatically, then cures at high temperature, creating a harder, more durable finish with better chip resistance than wet paint. Powder coating provides more uniform coverage, better corrosion protection, and is more environmentally friendly (no VOC emissions). Wet paint allows color matching to precise specifications and can be touched up in the field more easily than powder coating. For most industrial enclosures, powder coating provides superior performance and durability.
Can I modify an enclosure after it’s powder coated?
Minor modifications are possible but compromise finish quality. Drilling mounting holes after powder coating exposes raw metal edges that will rust unless touched up. Cutting large openings damages surrounding powder coat. For best results, complete all fabrication including mounting holes, cutouts, and hardware installation before powder coating. If field modifications are unavoidable, use touch-up paint matching the powder coat color to protect exposed metal.
How long does custom enclosure fabrication take?
Lead time depends on design complexity, material availability, shop workload, and finish requirements. Simple modifications to standard designs (adding custom cutouts or mounting holes) may take 2-3 weeks. Fully custom designs requiring engineering, prototyping, and tooling development typically need 6-12 weeks. Production runs of identical enclosures are faster per unit once initial setup is complete. Communicate timeline requirements early in the design process so fabricators can plan accordingly.
What’s the difference between NEMA 4 and IP66 ratings?
NEMA 4 and IP66 ratings are roughly equivalent but use different test methods. NEMA 4 requires protection against windblown dust and rain, resistance to external ice formation, and watertight construction preventing water entry during hosing. IP66 requires dust-tight construction (no dust ingress) and protection against powerful water jets from any direction. While generally equivalent, specific applications should verify that the rating standard matches their industry requirements—European customers often require IP ratings while North American customers specify NEMA.
How do I prevent condensation inside outdoor electrical enclosures?
Condensation forms when warm, humid air contacts cool surfaces, depositing moisture that damages electronics. Prevention methods include: thermostatically-controlled heaters maintaining interior temperature slightly above ambient (preventing condensation point), vapor barriers sealing the enclosure to prevent humid exterior air from entering, and desiccant breathers allowing pressure equalization while removing moisture from incoming air. For enclosures with air conditioning (common in telecommunications), insulated enclosures with vapor barriers are essential to prevent severe condensation.
What materials are best for corrosive environments?
Stainless steel (Type 304 or 316) provides the best corrosion resistance without coatings. Type 316 is superior for chloride exposure (salt water, road salt, chemical processing). For cost-sensitive applications, galvanized carbon steel with powder coating offers good corrosion protection at lower cost than stainless steel. Aluminum provides moderate corrosion resistance but may corrode in harsh industrial atmospheres without anodizing or coating. The environment severity determines whether premium materials like stainless steel are necessary or whether coated carbon steel suffices.
Can enclosures be ITAR compliant?
ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) regulates export of defense articles and technical data. An enclosure itself isn’t ITAR controlled—the equipment it contains determines ITAR applicability. However, fabricators producing enclosures for defense applications must be ITAR registered, implement security procedures protecting controlled technical data, and restrict facility access appropriately. EVS Metal maintains ITAR registration enabling work on defense-related projects.
What’s the advantage of using an ISO 9001 certified fabricator?
ISO 9001 certification demonstrates a fabricator’s quality management system meets international standards for consistent processes, documentation, and continuous improvement. For customers, this means: documented work procedures reducing errors, traceability from design through shipping, controlled handling of changes or deviations, and systematic corrective action when problems occur. While certification doesn’t guarantee perfection, it significantly reduces the risk of quality issues compared to non-certified fabricators.
How do I get started with a fabricated metal enclosure project?
Begin by documenting your requirements: What equipment will the enclosure contain? What environmental conditions will it face? What industry standards must it meet? Collect equipment dimensions, mounting requirements, cable entry needs, and any special features required. Then contact a fabricator with enclosure experience in your industry. EVS Metal’s engineering team can review requirements, suggest design approaches, and develop proposals including design concepts, estimated pricing, and lead times. Most enclosure projects benefit from early collaboration between customer and fabricator to optimize design before committing to production.
Choosing the Right Fabrication Partner for Industrial and Commercial Metal Enclosures
Fabricated metal enclosures protect critical equipment, ensure regulatory compliance, and enable reliable operation across diverse environments and applications. The difference between an enclosure that performs reliably for decades and one that fails prematurely often comes down to proper specification, material selection, and fabrication quality.
EVS Metal combines advanced manufacturing capabilities, engineering expertise, industry certifications, and over 30 years of precision fabrication experience to deliver custom metal enclosures meeting the most demanding requirements. From simple modifications of standard designs to fully engineered custom solutions, we provide the complete fabrication services required to transform concepts into production reality.
Ready to discuss your commercial or industrial metal enclosure project? Contact EVS Metal today. We’ll review your application requirements, recommend optimal design approaches, and develop a solution delivering the protection, quality, and performance your equipment demands.

 Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and Durability